Cardiovascular Health Resource Library
Find guidance, case studies, advocacy tools and more for large-scale heart health programs

You’ve been redirected. LINKScommunity.org is now part of resolvetosavelives.org.
Filter by country:
Using simple, practical treatment protocols standardizes a high quality of care and significantly improves health outcomes in large-scale hypertension control programs. Not only do they provide easy-to-follow, step-by-step instructions that empower non-physician health care workers to manage patient care closer to home, they also unlock bulk purchasing for essential medications, lowering costs and the risk of drug shortages and making it easier for patients to stay on treatment,
These universal hypertension treatment protocols, created by clinical experts at Resolve to Save Lives, offer options that countries can adapt to their local context and include the addition of statins to simultaneously treat high cholesterol and further reduce risk factors for heart attack and stroke.
A new paper in Global Hearts co-authored by RTSL advocates for integrating hypertension medicines and cholesterol medicines into treatment plans to address the 90% of patients in low- and middle-income countries who don’t receive the cholesterol medications they need for primary cardiovascular disease prevention. Including statin treatment within existing HEARTS hypertension and diabetes protocols can help expand coverage and close this treatment gap.
Abstract
In low- and middle-income countries where the majority of preventable cardiovascular disease deaths occur, less than 10% of eligible patients receive statins for primary cardiovascular disease prevention. Since 2017, the Global Hearts initiative has implemented simple World Health Organization (WHO) HEARTS hypertension and diabetes treatment protocols. In this editorial, we propose an approach of integrating statin treatment into existing HEARTS hypertension and diabetes protocols as a way of expanding statin coverage in low-and middle-income countries.
Faulty blood pressure readings can put lives at risk. A new randomized clinical trial shows that commonly used arm positions (lap or side) result in substantially higher blood pressure readings which can lead to false diagnoses and over-treatment. To measure blood pressures accurately, the arm should be supported at heart level. The authors call for clinical guidelines to include this new evidence-based knowledge.
Question What is the effect of commonly used arm positions on blood pressure (BP) measurements compared to the standard, recommended position?
Findings This crossover randomized clinical trial of 133 adults showed that supporting the arm on the lap overestimated systolic BP by 3.9 mm Hg and diastolic BP by 4.0 mm Hg. An unsupported arm at the side overestimated systolic BP by 6.5 mm Hg and diastolic BP by 4.4 mm Hg, with consistent results across subgroups.
Meaning Commonly used, nonstandard arm positions during BP measurements substantially overestimate BP, highlighting the need for standardized positioning.
Importance Guidelines for blood pressure (BP) measurement recommend arm support on a desk with the midcuff positioned at heart level. Still, nonstandard positions are used in clinical practice (eg, with arm resting on the lap or unsupported on the side).
Objective To determine the effect of different arm positions on BP readings.
Design, Setting, and Participants This crossover randomized clinical trial recruited adults between the ages of 18 and 80 years in Baltimore, Maryland, from August 9, 2022, to June 1, 2023.
Intervention Participants were randomly assigned to sets of triplicate BP measurements with the arm positioned in 3 ways: (1) supported on a desk (desk 1; reference), (2) hand supported on lap (lap), and (3) arm unsupported at the side (side). To account for intrinsic BP variability, all participants underwent a fourth set of BP measurements with the arm supported on a desk (desk 2).
Main Outcomes and Measures The primary outcomes were the difference in differences in mean systolic BP (SBP) and diastolic BP (DBP) between the reference BP (desk 1) and the 2 arm support positions (lap and side): (lap or side − desk 1) − (desk 2 − desk 1). Results were also stratified by hypertensive status, age, obesity status, and access to health care within the past year.
Results The trial enrolled 133 participants (mean [SD] age, 57 [17] years; 70 [53%] female); 48 participants (36%) had SBP of 130 mm Hg or higher, and 55 participants (41%) had a body mass index (calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared) of 30 or higher. Lap and side positions resulted in statistically significant higher BP readings than desk positions, with the difference in differences as follows: lap, SBP Δ 3.9 (95% CI, 2.5-5.2) mm Hg and DBP Δ 4.0 (95% CI, 3.1-5.0) mm Hg; and side, SBP Δ 6.5 (95% CI, 5.1-7.9) mm Hg and DBP Δ 4.4 (95% CI, 3.4-5.4) mm Hg. The patterns were generally consistent across subgroups.
Conclusion and Relevance This crossover randomized clinical trial showed that commonly used arm positions (lap or side) resulted in substantial overestimation of BP readings and may lead to misdiagnosis and overestimation of hypertension.
Trial Registration ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT05372328
In this new guide from Resolve to Save Lives, large-scale hypertension programs can better find patients who are overdue for a health visit and bring them back to care. Reducing loss to follow-up is a leading way to improve hypertension control and reduce deaths from heart attacks and strokes. Phone calls, text messages, and home visits keep patients retained in treatment.
Program managers can use this resource to support their staff to track and manage overdue patients and successfully get them the care they need.
Other related resources:
- Designing an optimal digital tool for hypertension and other long-term treatment programs
- Phone Calls to Overdue Patients with Hypertension – factsheet
- Leading a Good Data Review Meeting – full guide and factsheet
- Change Package: Overdue Patient Management
Download the new DHIS2 hypertension and diabetes control package—a free, open-source health management data platform developed by DHIS2 and Resolve to Save Lives.
DHIS2 Tracker is a free, open-source health management data platform developed by DHIS2 and Resolve to Save Lives that program managers can use to monitor large-scale non-communicable disease (NCD) programs. The new version 2.0 integrates hypertension and diabetes care and is optimized for use in busy primary care facilities that manage thousands of patients. DHIS2 is quick and simple enough to record individual patient data during clinical care and records only the data you need to treat patients effectively and monitor outcomes. Not only is DHIS2 a practical, sustainable, ready-to-use solution, but it’s cost-effective and easy-to-train, too.
Over 70 countries rely on DHIS2 to manage health programs for TB, malaria, Covid-19, MCH, vaccinations, and more, and Nigeria now uses it to manage their large-scale NCD program. Your country can be next.
This factsheet offers key features and a use-case from Nigeria.
Learn more about true user-centered care and the Digital team at Resolve to Save Lives.
Demo the new DHIS2 hypertension and diabetes control package—a free, open-source health management data platform developed by DHIS2 and Resolve to Save Lives.
Resolve to Save Lives’ partnerships for heart health between 2018 and 2023 will result in 7.5 million fewer deaths worldwide. Here’s how we supported countries to make rapid progress, and how we measured our impact.
New World Health Organization progress report, supported by RTSL.
Since initial call to action in 2018 for all countries to eliminate toxic trans fat and protect their people from this risk factor for heart attack and strokes, 43 more countries have banned trans fat protecting an additional 2.8 billion people, or 46% of the world—as compared to just 6% 5 years ago. The REPLACE technical package provides guidance on best-practice policies that governments can implement today to protect the remaining 54% of the world from this harmful but easily replaceable food additive.
Virtual course developed by PAHO aiming to strengthen capacity to design and advance effective regulatory policies that reduce the demand for and offer of ultra-processed and processed products to prevent obesity and diet-related NCDs in the Region of the Americas.
Nutrition standards guide developed by Resolve to Save Lives that governments can use to ensure food and beverages purchased, served and/or sold in government settings such as schools, public hospitals, childcare or child development facilities, correctional facilities and government workplaces are healthy and low in sodium.
Sodium reduction is the single most important dietary intervention for improving heart health and saving lives. Learn more in this resource developed by Resolve to Save Lives.
Playbook with step-by-step guidance for creating an effective digital tool for hypertension management and other chronic disease programs
Core principles, benefits and resources for implementing healthy food procurement and service policies.
Step-wise framework for monitoring, includes: 1) previous monitoring activities of school food programs, and 2) survey questions for initial assessment.
The policy index measures the extent of implementation of health food environment policies by governments compared to international best practice and includes a module on Food Provision. Scientific article describes in detail: L’Abbe M, Schermel A, Minaker L, Kelly B, Lee A, Vandevijvere S, Twohig P, Sarquera S, Friel S, Hawkes C, et al. Monitoring foods and beverages provided and sold in public sector settings. Obesity Reviews. 2013;14(Suppl. 1):96–107l.
Systematic review of the evidence base for healthy food procurement policies
Toolkit for communications and advocacy activities to accelerate the adoption of trans fat elimination policies, including social media resources and customizable templates
WHO’s first-ever report on the global burden of high blood pressure and the progress made to manage the disease.
In the Journal of American College of Cardiology International, a summary of success, progress, and lessons learned during the first five years of the HEARTS initiative.
There are five crucial components of hypertension care at public health scale: simple treatment protocols; access to quality, affordable medications, team-based care and task sharing; patient-centered care; and strong information systems.
This framework summarizes the recommended components of a comprehensive dietary sodium reduction program, and provides links to existing implementation tools, examples of successful programs and other resources.
Series of case studies documenting experiences from around the world with the implementation and enforcement of trans fat regulations
Fact sheet from Resolve to Save Lives with practical steps for countries to develop and implement best practice trans fat elimination policies
A practical guide to a patient-centered approach to integrating hypertension and HIV care using differentiated service delivery
A hypertension and diabetes control package for the District Health Information System 2 (DHIS2)—a free, open-source health management data platform.
Not only is DHIS2 a practical, sustainable, ready-to-use solution, but it’s cost-effective and easy-to-train, too.
Developed by the Federal Ministry of Health in Nigeria in collaboration with WHO-Nigeria and the University of Oslo, the newly updated DHIS2 hypertension/diabetes program (v2) and DHIS2 Android app (v3.0) are now available, meaning DHIS2 is optimized for use in busy primary care facilities managing thousands of patients with hypertension and diabetes, is quick and simple enough to record individual patient data during clinical care, and records only the data you need to treat patients effectively and monitor outcomes. Program managers can use the HEARTS360 dashboard to monitor WHO HEARTS indicators for large-scale non-communicable disease (NCD) programs. The DHIS2 package is now available to any country in the world.
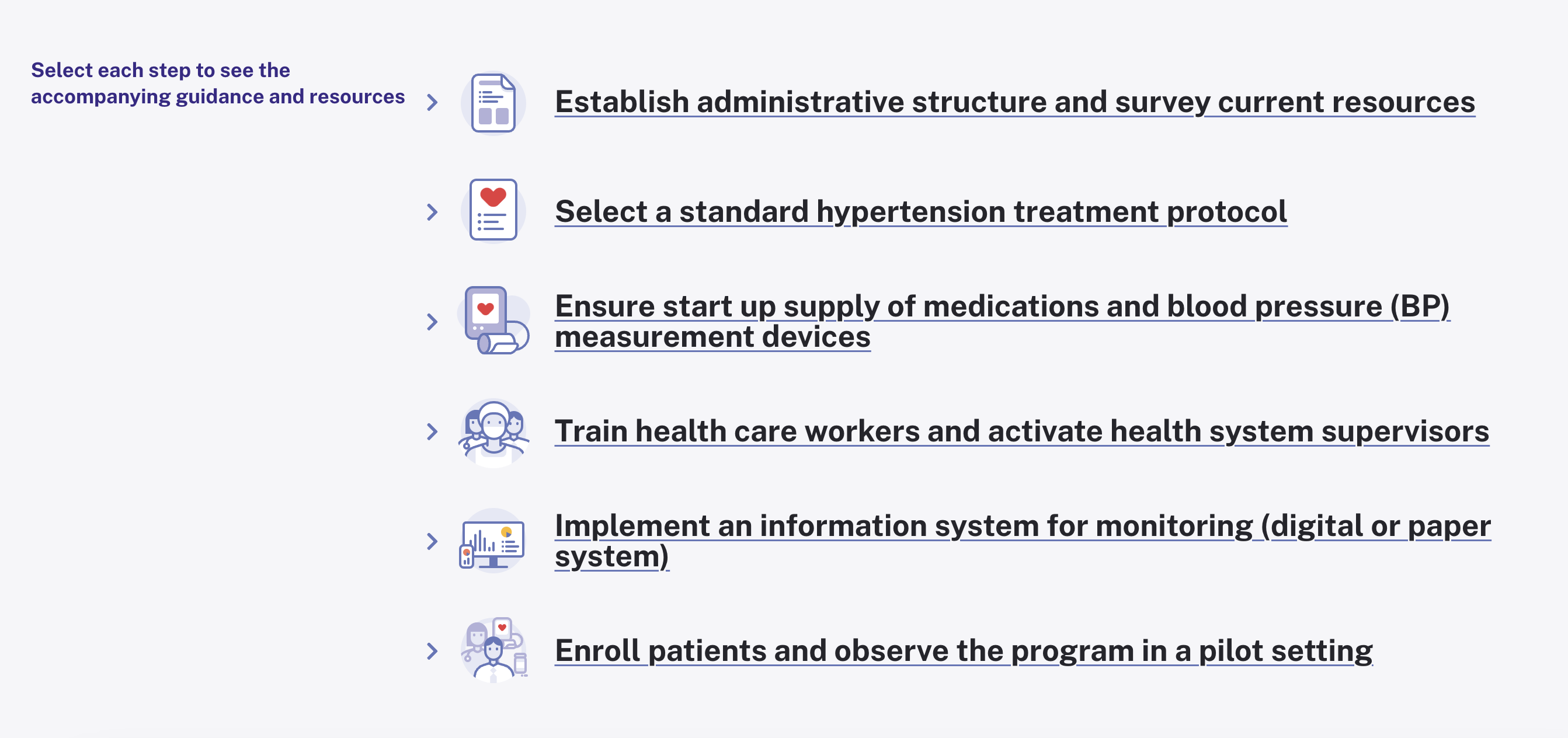
Fact sheet from Resolve to Save Lives with six steps to implementing a successful national hypertension control program.
Fact sheet from Resolve to Save Lives on the status of trans fat elimination policies globally
Our report, developed in collaboration with the Médecins Sans Frontières Access project, identifies barriers to affordable blood pressure medication in LMICs and underscores the need for a transformation of the global blood pressure medicines market to make life-saving medicines more affordable and available.
Describes five key elements of a healthy diet.
This paper sets out an approach to measure the implementation of the WHO Global Strategy on Diet, Physical Activity and Health (DPAS) at country level and proposes a framework and indicators for this purpose. The indicators provided in this document should be seen as examples to be used, as appropriate, after adjusting to the country reality. The proposed framework and indicators are intended to provide a simple and reliable tool for Member States. The indicators are also intended to be flexible and adaptable to national circumstances and to take into account existing as well as planned activities in surveillance and monitoring.
Results of global survey on school meals; report identifies key aspects to consider when developing or updating school meal program standards.
Searchable database of implemented policies to promote healthy diets and reduce obesity. Use Section O (Offer healthy food and set standards in public institutions and other specific settings) to search for public food procurement examples.
A template for organizational food policy guidelines adapted from the CDC
Model policies for policymakers. Website links to resources on creating healthy food service on government property and an infographic on buying food for health and equity.
Provides an overview of how to develop, implement, assess compliance with, and evaluate the effectiveness of a healthy public food procurement and service policy. It is intended for government policy makers or program managers working on public food procurement or service, at either a national or a subnational level, including at regional, provincial and city levels.
Fact sheet from Resolve to Save Lives on healthier replacement oils
Website with all materials related to WHO’s REPLACE initiative
Sampling protocol from Resolve to Save Lives and Global Health Advocacy Incubator
Map from WHO showing status of trans fat elimination around the world
Annotated bibliography from Resolve to Save Lives. Updated 5/2018.
A document that updates the global sodium benchmarks developed in 2021 for different food categories to help reduce salt intake using country experiences (updated in 2024)
Step-by-step guide to developing front-of-package labels
An article identifying high priority strategies that address reduction of sodium intake through home-cooked food, packaged food, food consumed outside the home
A nine-module online course to help policy makers and health advocates design, plan, and implement global sodium reduction interventions at low- and middle-income countries
A report on key recommendations and advice to policymakers who are designing and implementing front-of pack food labelling in nutrition policies
A resource that provides guidance for governments on how to develop, implement, and strengthen a healthy public food procurement or service on a national or sub-national level
Summarizes RTSL’s approach to sodium reduction, including two page summaries for key interventions (sodium targets, FOPL, food procurement and service, low sodium salt, policy advocacy and communications)
A technical package from WHO designed to assist countries with the development, implementation, and monitoring of salt reduction strategies to reduce population salt intake
A collection of literature relevant to the science of salt reduction and on sodium reduction interventions
Our guide for program managers starting up national or subnational hypertension control programs, broken down into six steps and and supported by practical tools from our hypertension control resource library and the WHO HEARTS technical package and adaptable to the local program and setting.
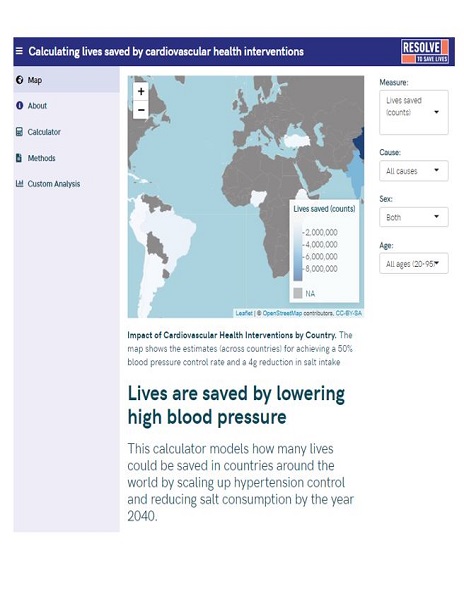
Calculator modeling the impact of cardiovascular health interventions (including improved hypertension control) by country
WHO’s technical package for cardiovascular disease management in primary health care
WHO report assessing global progress in implementing sodium reduction policies, providing insights by country, region, and income group to guide future actions for reducing sodium intake and improving cardiovascular health.
This guideline offers evidence-based recommendations for reducing sodium intake to prevent NCDs, supporting policymakers and program planners in assessing intake levels, developing interventions, and aligning efforts with global health targets.
National treatment guideline adopted in Nigeria to support the management of high blood pressure and improve access to medications.
A quality improvement (QI) initiative conducted by the India Hypertension Control Initiative (IHCI) between January 2021 and September 2022 led to an increase in monthly follow-up visits from 21% to 37% and a decrease in missed health visits from 66% to 22%. Of the individuals counseled by ASHA home visits, 74.9% returned for follow-up. The QI initiative organized a multidisciplinary team to identify major root causes for missed visits—such as not effectively mobilizing patients for follow-up visits— and develop countermeasures—such as improved tracking as use of ASHA home visits. Health care workers were trained in the interventions, and a simple, digital health tool captured real-time data to follow progress of interventions in monthly data review meetings once they were implemented.
ABSTRACT
Background In India, to achieve a 25% relative reduction in the prevalence of raised blood pressure (BP) by 2025, approximately 4.5 crore additional people with hypertension will need to have their BP effectively treated. We conducted a Quality Improvement (QI) initiative to improve follow- up and reduce missed visits among individuals with hypertension registered under India Hypertension Control Initiative, District Hospital, Seoni, Madhya Pradesh, India, in 2022.
In a new article published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA), Dr. Tom Frieden and colleagues call for a focused strategy and more investment to address the world’s leading killer diseases. The article outlines specific, effective, and measurable steps countries can take to make progress and increase the chances that the upcoming 2025 United Nations High-Level Meeting on Noncommunicable Diseases delivers results:
- Increase taxes on tobacco, alcohol, and sugary beverages to prevent 50 million premature deaths over the next 50 years and generate $20 trillion in revenue
- Expand hypertension treatment to prevent up to 130 million deaths over 35 years
- Scale up cancer prevention, early detection, and treatment, including widespread HPV vaccination
- Reduce air pollution through cleaner energy transitions and stricter emissions regulations to prevent at least 10 million deaths
- Improve nutrition by mandating front-of-package warning labels and reducing sodium intake.
Once a best-practice trans fat elimination policy is passed and adopted, it must be implemented and enforced. This advocacy document developed by Resolve to Save Lives serves as a guide for the monitoring and enforcement of best practice policies that eliminate industrially produced trans fat from a country’s food supply.
A two-page advocacy brief developed by Resolve to Save Lives to highlight the key elements of WHO’s HEARTS technical package for managing cardiovascular disease:
Just switching from regular salt to low-sodium alternatives can save lives. WHO now recommends this life-saving strategy pioneered by Resolve to Save Lives to reduce salt intake and its associated health risks.
The only resource of its kind, Resolve to Save Lives’ (RTSL) new and improved Global Nutrition Database now includes 55 datasets covering the sugar, sodium, and saturated fat content of packaged foods from 36 countries. The updated database provides more detailed information on national packaged food policies in each country, as well as the updated WHO global sodium benchmarks (2nd edition) and the updated PAHO regional sodium targets, allowing for improved comparisons to regional and global targets. This resource can support research and advocacy efforts to advance nutrition policies in your country or region.
In a Data for Action: Harnessing the new RTSL Global Nutrition Database to shape healthier packaged food policies, a webinar to launch the update, nutrition experts from RTSL and our partners explore the new Global Nutrition Database and the important role data on packaged food contents to develop, implement, and monitor packaged food policies worldwide. Country experiences offer insight into using data to advocate for healthier food environments in varying local contexts.
Panelists and presenters:
- Nora Abdel-Gawad (Resolve to Save Lives) – RTSL’s Global Nutrition Database
- Dr. Mary L’Abbe (L’Abbe Labs, University of Toronto) – Multi-country insights using the FLIP database and application
- Dr. Ge Zeng (Vital Strategies – China) – Sodium target monitoring and data collection
- Dra. Gabriela Flores (University of Buenos Aires) – Salt target surveillance and compliance
A new analysis by Resolve to Save Lives and partners is clear: removing patient copayments for anti-hypertensive medications reduces risk of heart attack, stroke, and hospitalization. Countries should explore providing free blood pressure medications as a way to save lives and meet sustainable development goals, particularly in LMICs where 80% of hypertension-related deaths occur and costs remain a significant barrier to achieving blood pressure control and reducing risk.
Infographic from Resolve to Save Lives highlighting key points from “Use of lower-sodium salt substitutes: WHO guideline,” why it matters, and what it means for countries.
Detailed user guide to supplement use of Resolve to Save Lives’ Global Nutrition Database for Packaged Foods, an online, open access, centralized platform for category level packaged food data that policy advocates and decisionmakers can reference when developing food policies or tracking country progress.
A comprehensive assessment of the existing food procurement landscape is crucial to the development, implementation, and evaluation of a healthy public food procurement policy that is relevant to the specific context. Resolve to Save Lives has developed example surveys for capturing key aspects of the food procurement and policy landscape. These surveys should be adapted to each local context. Example surveys in this series include:
- Survey 1: Overview of Government Institutions’ Food Procurement Processes
- Survey 2: Key Informant Interview Tool
- Survey 3: Detailed Assessment of the Food Environment in Government Settings
Survey #1 can be used to identify the government institutions that purchase, serve, and/or sell food. Then, for institutions that do purchase, serve, and/or sell food, Survey #2 and #3 can be used for a more detailed follow-up assessment of the food environment and to better understand the food procurement process.
This new systematic review demonstrates that standardized and simplified hypertension treatment protocols significantly reduce high blood pressure compared with usual hypertension care. Simple hypertension management protocols streamline treatment steps, improving outcomes for patients and making medications more available and affordable.
ABSTRACT
Large gaps persist in the diagnosis, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension globally. Standardized treatment protocols (STPs) have been widely proposed to guide hypertension treatment, particularly in primary healthcare settings. However, there has been no review that quantifies the effects of hypertension STPs on blood pressure (BP) reduction and control. We conducted a systematic review of randomized clinical trials (RCTs) among adults with hypertension, comparing hypertension STPs (intervention) with usual care (comparator) for effects on BP. Relevant RCTs were identified by searching multiple electronic databases. Random-effects meta-analyses were conducted to evaluate between-group differences in systolic BP reduction (primary outcome), diastolic BP reduction, BP control, and adverse events (AEs). Sixteen RCTs involving 59,945 participants (baseline mean BP: 149/91 mmHg) were included. Reductions in systolic and diastolic BP with STPs compared to usual care were 6.7 (95% CI 3.7–9.8) mmHg and 2.6 (1.2–4.1) mmHg, respectively (p < 0.001 for both). BP control achieved was 57% in the STP group compared to 24% in the usual care group (p < 0.001). The overall incidence of any AEs was 14.5% versus 13.5% (RR 1.27 [0.88–1.82]) with STPs and usual care, respectively. In summary, interventions involving hypertension STPs significantly reduce systolic and diastolic BP and improve BP control compared to usual care. STPs can, therefore, be an efficient strategy to implement evidence-based treatments and upscale treatment coverage, given the large untreated and uncontrolled hypertension burdens globally.
This study, co-authored by the RTSL nutrition team, uses focus groups of consumers in Bangladesh to better understand purchasing decisions and effectiveness of nutrition labels. Chief food purchase concerns include that a food has sufficient beneficial nutrients, is free from germs or toxins, and does not contain high levels of nutrients of concern. Results suggest that front-of-package labels would help consumers more easily identify unhealthy foods and that warning labels were perceived as more effective than color-coded labels.
Abstract:
A new study in BMC conducted and funded by RTSL’s partners in Thailand analyzes trends in hypertension prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control in Thailand over the past 15 years. Despite significant strides such as the adoption of universal health coverage, hypertension awareness and blood pressure control remain a challenge throughout Thailand. An urgent and concerted public health response is needed to improve diagnosis and control of hypertension to prevent premature deaths from this leading killer.
Resolve to Save Lives works closely with governments to improve heart health and save lives from high blood pressure, the world’s leading killer. Learn more here.
Clear and accurate nutrition labeling on food products is an important way for consumers to understand what’s in the foods they buy. This new comprehensive review in Frontiers led by partners at the National Heart Foundation of Bangladesh and co-authored by Resolve to Save Lives shows that governments are scaling up action to help consumers make informed food choices especially through front-of-package labels (FOPL). Research in the field shows that the most effective FOPL is mandatory; uses a black and white warning label design to flag products high in sodium, sugar, and saturated fat; and is developed free from any conflicts of interest.
Learn more about RTSL’s work to create healthier food environments here, or browse our library of key resources.
A resource outlining Vital Strategies’ Breakthrough model for planning strategic communication campaigns to achieve measurable public health outcomes.
Models how many lives could be saved in countries around the world by scaling up hypertension control and reducing salt consumption by the year 2040
Overview of front-of-package warning labelling policies around the world developed by GHAI
Centralized location for industry alerts, policy briefs, and reports to help organizations stay up-to-date on the ultra-processed food and beverage industry.
Collection of advocacy resources on various health food policies such as Front-of-Package Warning Labels, Marketing Restrictions, Sugar-Sweetened Beverage Taxes, and Trans fatty Acids Eliminations.
Guide developed by the Global Health Advocacy Incubator (GHAI) to provide public health advocates with strategies, case studies, and lessons from over 40 countries to plan, organize, and implement effective advocacy for health policy outcomes.
The NOURISHING database, built on the NOURISHING policy framework, offers a comprehensive set of policies to guide policymakers, researchers, and civil society in promoting healthy diets and combating obesity and NCDs across ten key action areas.
Provides centralized access to category level nutrient data for packaged foods sold around the world
A recent analysis authored by RTSL and our partners in India shows a lack of awareness among private sector providers in India that high blood pressure is a critical health threat. Providing prescriptions to patients is the first step in increasing medication availability and affordability. To encourage evidence-based hypertension care, the government and NGOs could implement strategies such as tailored incentives, financial rewards, tax benefits, accreditation, and recognition for private healthcare providers who prioritize controlling high blood pressure. Professional bodies in the private sector should establish programs emphasizing quality assurance and certifications in this area. Future research should focus on designing and testing new models for private sector hypertension service delivery.
This two-page factsheet outlines the key takeaways from the full guide, Guide for Management of Overdue Patients with Hypertension, and is designed as a resource for staff in your hypertension clinic.
Other related resources:
- Designing an optimal digital tool for hypertension and other long-term treatment programs
- Leading a Good Data Review Meeting – full guide and factsheet
- Change Package: Overdue Patient Management
This one-page factsheet outlines the key takeaways from the full guide, Leading a Good Data Review Meeting, and is designed as a resource for staff in your hypertension clinic.
Other related resources:
The ultimate goal of a successful hypertension program is to improve blood pressure control at the population level. Establishing regular data review meetings to review program progress using the HEARTS360 dashboard can enhance decision-making and build a culture of quality and accountability for large-scale hypertension programs. Use the following four steps to identify, address, and track barriers to blood pressure control within your hypertension program.
Other related resources:
- Designing an optimal digital tool for hypertension and other long-term treatment programs
- Guide for Management of Overdue Patients with Hypertension
- Leading a Good Data Review Meeting – factsheet
- Phone Calls to Overdue Patients with Hypertension – factsheet
- Change Package: Overdue Patient Management
Program managers of large-scale hypertension programs can use the evidence-based interventions outlined in this new resource from Resolve to Save Lives to better track and manage patients overdue for a visit—and return them to care.
Other related resources:
NCD report highlighting common best practice fiscal policies consistent with NCD prevention as well as measures that are recommended as highly effective in reducing the enormous strain of NCDs.
By bringing care delivery closer to communities, we can provide more people with access to quality care, improve hypertension control and save more lives. Our experts in India documented the decentralization process and its impact on patient outcomes in nine districts from 2018–2022.
Improving hypertension control requires patient retention to hypertension treatment, which requires ready access to care. This study highlights the need for improved primary care services and patient-centered services, including extended clinic hours and diagnostic facilities.
Experts from Resolve to Save Lives India analyzed patient retention rates in hypertension treatment using a mixed-method concurrent design in a North Indian district, considering socio-demographic characteristics and patient follow-up rates along with focus group discussions and in-depth interviews with health care providers and patients. Patient retention and blood pressure control were better at Health and Wellness Centers (HWCs) levels; barriers such as medication side effects, pill burden, and limited health care access hindered patient retention and medication adherence, compromising hypertension control at higher-level facilities, notably among females.
“The decentralization process involved training, treatment protocol provision, supervision, and monitoring. Among 394,038 individuals registered with hypertension from 2018–2021, 69% were under care in 2022. Nearly half of those under care (129,720/273,355) received treatment from HWCs in 2022. Care of hypertensive individuals from district hospitals (14%), community health centres (20%), and primary health centres (24%) were decentralized to HWCs. Overall BP control rose from 20% (4,004/20,347) in 2019 to 58% (157,595/273,355) in 2022, while missed visits decreased from 61% (12,394/20,347) in 2019 to 26% (70,894/273,355) in 2022. This trend was consistent in both states. HWCs exhibited the highest BP control and the lowest missed visits throughout the study period compared to other facility types.”
Read the full study here.
Authors: Nidhi Jaswal PhD, Sonu Goel PhD, Kritika Upadhyay MPH, Anupam Khungar Pathni MBBS, Om Prakash Bera MPH, MBA, Vandana Shah LLM
Learn how integrating hypertension management in HIV services improved health outcomes in India.
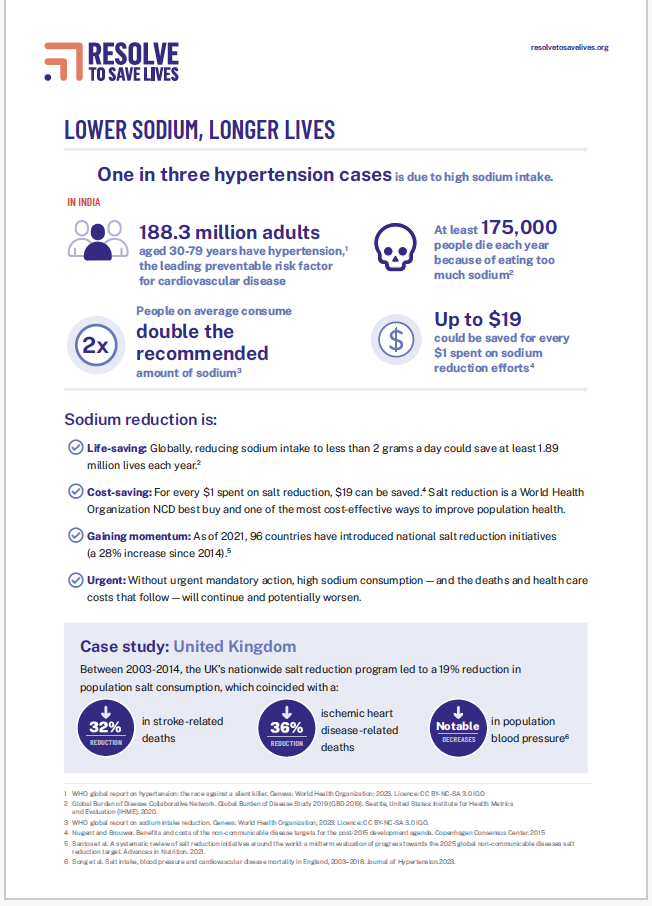
Sodium reduction is the single most important dietary intervention for improving heart health and saving lives in India. Learn more in this resource developed by Resolve to Save Lives.
Learn more about Resolve to Save Lives’ comprehensive, cost-effective interventions to promote healthier diets and save lives in India.
Learn more about how Resolve to Save Lives is working to end preventable deaths from cardiovascular disease in India.
A WHO guideline offering Member States recommendations on implementing fiscal policies, such as taxes and subsidies, to promote healthy diets by influencing consumer behavior through price adjustments at the retail level.
WHO’s updated list of “best buys” and recommended interventions for addressing NCDs, aligned with the extended Global Action Plan (2013–2030) to help countries achieve the nine voluntary NCD targets and advance SDG 3 on good health and well-being.
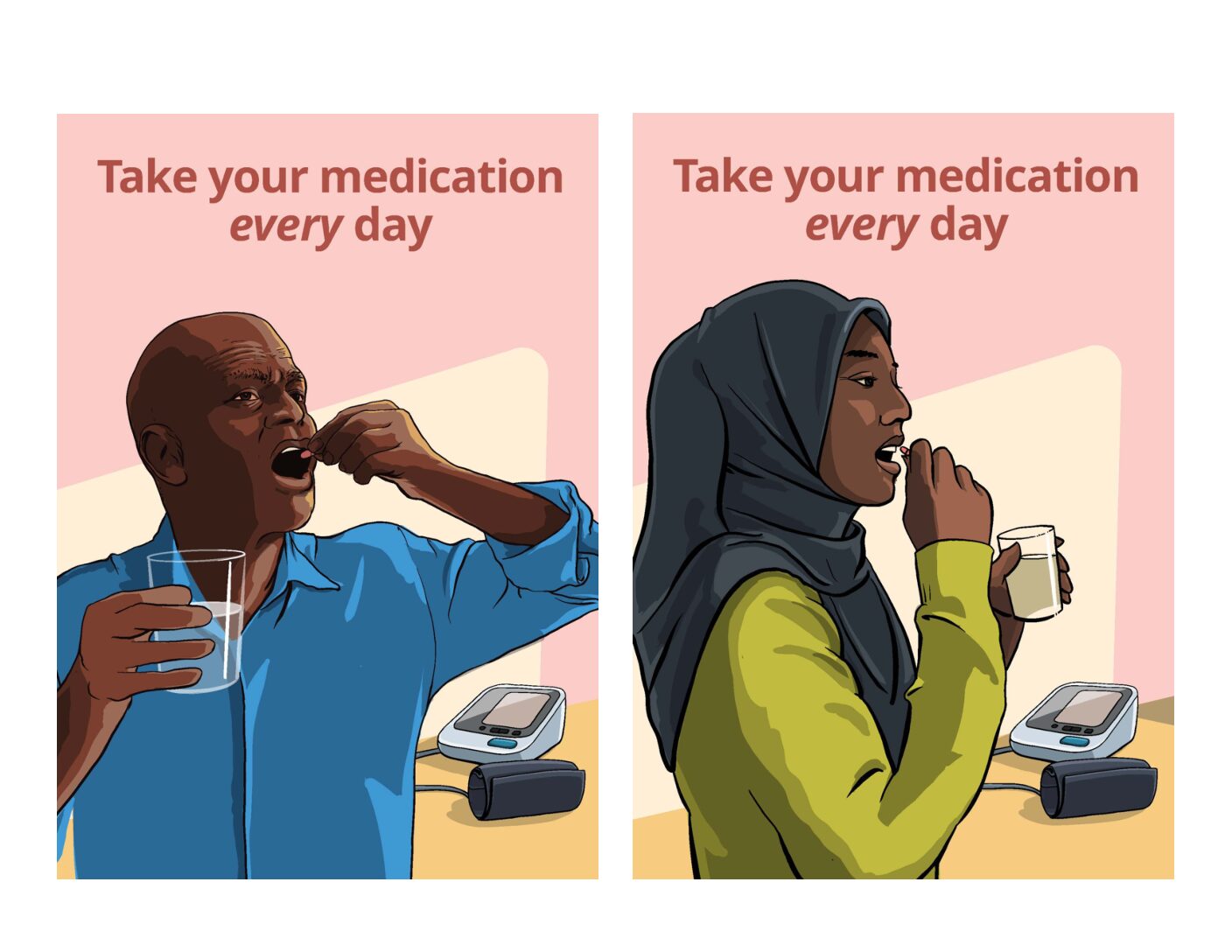
A qualitative study conducted by Resolve to Save Lives determined this poster to be the most impactful for encouraging patients to take their blood pressure medications daily. Forty patients from five different places said they prefer this poster because it shows someone actually taking their medication, which made clear what they needed to do.
A six-step guide developed by Resolve to Save Lives that governments can follow to help reduce sodium consumption at the national level.
Fact sheet from Resolve to Save Lives making the case for trans fat regulation in low-burden settings
Fact sheet highlighting the addition of low-sodium salt to one’s diet to reduce blood pressure and associated risk of heart attack or stroke.
Position paper from GHAI, Resolve to Save Lives and other partners presenting best practices for defining, selecting and using effective NPMs.
Includes resources to support transitioning to healthier school canteens for school leaders, canteen managers, parents, and communities.
Best practice guidelines for health facilities to use for cafes/cafeterias, vending machines, convenience stores/newsagents, retail premises, and catering.
Standards for food and drinks available to staff, volunteers, and visitors for ACT Health premises; links to Healthy Food and Drink Choices and Vending Machine Management Policies.
Cardiovascular Health
Hypertension Control
Sodium Reduction
Trans Fat Elimination
Cardiovascular Health Resource Library
Find guidance, case studies, advocacy tools and more for large-scale heart health programs