Ethiopia National Infection Prevention and Control Policy

The Ministry of Health Ethiopia, in collaboration with all relevant stakeholders; in line with internationally acclaimed standardized recommendations has developed this National Infection Prevention and Control Policy for Health Care Services to assist health care workers and other IPC stakeholders in the design, implementation, monitoring, and evaluation of IPC programs in Ethiopia. The Ministry remains […]
Ethiopia National Infection Prevention and Control Program (IPC) Monitoring and Evaluation Plan 2021/22-2025/26

This IPC Monitoring and Evaluation Plan 2021-2026 from Ethiopia’s Ministry of Health was developed to be used at all levels of the health care system and will help to measure and monitor the progress of the implementation of the national IPC Policy, Strategy recommendations and Strategy Roadmap activities including the IPC practices at health facility […]
Ethiopia National Healthcare Associated Infections (HAIs) Surveillance Guideline

Ethiopia National Healthcare Associated Infections (HAIs) Surveillance Guideline is intended to serve as a guide for health care professionals in general, and for IPC professionals in particular, to ensure that the critical elements and methods of surveillance for health care-associated infections (HAIs) are incorporated into their practice. It provides guidance for each of the surveillance […]
Ethiopia National Infection Prevention and Control Strategy and Roadmap 2021/22-2025/26

Ethiopia’s national IPC strategy and roadmap for 2021-2026 is intended to guide and outline the strategic interventions required to prevent, reduce and control the development of health care-associated infections (HAIs) and antimicrobial resistance (AMR), ultimately improving patient safety and health outcomes.
Ethiopia national IPC reference manual, Volume 2: Advanced and special settings

Full title: National infection prevention and control reference manual for healthcare service providers and managers, Volume 2: Advanced and special settings infection prevention and control, Third edition. The manual is divided in two volumes: Volume I covers general IPC and Volume II addresses more advanced IPC and special settings. The document serves as a standardized […]
Ethiopia national IPC reference manual, Volume 1: General infection prevention and control

Full title: National infection prevention and control reference manual for healthcare service providers and managers, Volume 1: General infection prevention and control, Third edition. The manual is divided in two volumes: Volume I covers general IPC and Volume II addresses more advanced IPC and special settings. The document serves as a standardized IPC reference manual […]
Unleashing the full potential of 7-1-7

A strategic guide for international partners on the powerful system improvement tool that drives accountability, reveals bottlenecks, and informs targeted investments.
From signals to systems: Strengthening epidemic readiness through climate-informed strategies
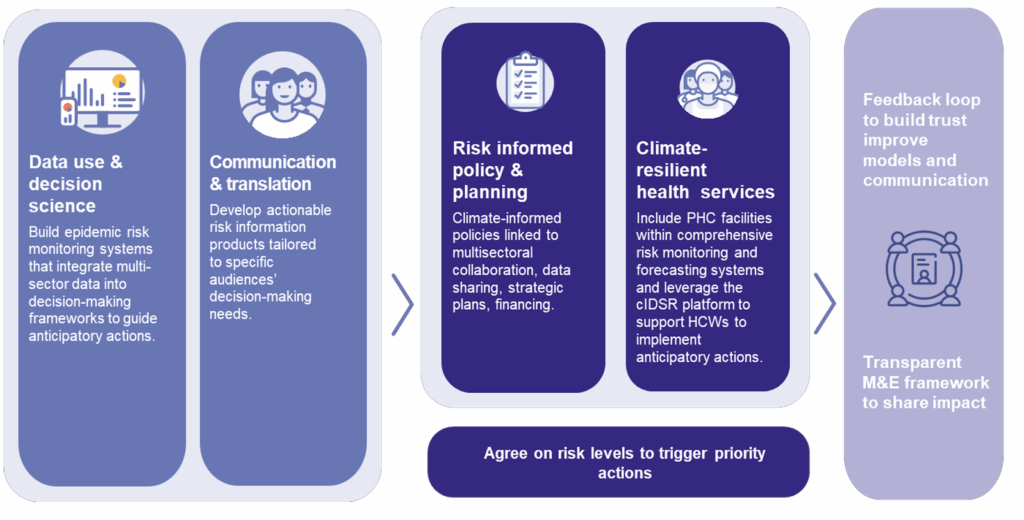
This issue brief outlines how Resolve to Save Lives is supporting governments to strengthen epidemic readiness by integrating climate data into health systems. Key strategies include building epidemic risk monitoring systems using real-time climate data, improving communication of climate-health risks, embedding climate-sensitive protocols into health policy and developing resilient primary health care infrastructure. These efforts […]
Foundations for sustainable health: A blueprint for building epidemic-ready and climate-resilient primary health care

This blueprint outlines our model for epidemic-ready, climate-resilient and sustainable primary health care infrastructure using an all-hazard approach. We urge national governments to embed resilience into health and infrastructure planning. We call on donors to support integrated, scalable investments and help countries learn from what works. And we encourage facility leaders and communities to codesign and […]
From 18 countries to yours: Actionable 7‑1‑7 bottleneck insights

The 7-1-7 Alliance to identifies global patterns in the barriers to outbreak detection, notification and response and provides an example of how countries can leverage their own 7-1-7 bottleneck data to inform investments, prioritization and accelerate performance improvement.
Epidemic-Ready Primary Health Care (ERPHC) framework and technical package
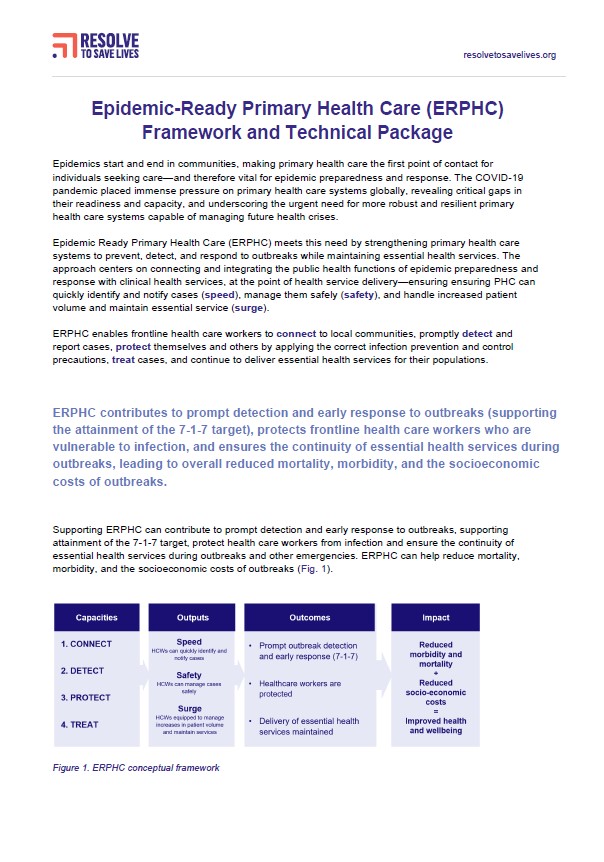
This technical toolkit explains how Epidemic-Ready Primary Health Care (ERPHC) ensures PHC systems can quickly identify and notify cases (speed), manage them safely (safety), and handle increased patient volume and maintain essential service (surge). It outlines capacities, core activities and outcomes for implementation and includes a proposed implementation model.
Actionable 7‑1‑7 bottleneck insights: Resources for rapid outbreak investigation

This resource from the 7-1-7 Alliance is part of a series that highlights the value of effective bottleneck analysis with 7-1-7 and brings to the front solutions to the top barriers to outbreak detection, reporting and response.
Development and Implementation of a Public Health Event Management System, Nigeria, 2018–2024

In a study published in Emerging Infectious Diseases, Resolve to Save Lives and colleagues explore the role of event management systems (EMS) in epidemic intelligence, focusing on the Nigeria Centre for Disease Control and Prevention’s (NCDC) SITAware software. EMS are essential for integrating surveillance signals and managing incident response, though international standards for their development […]
Strengthening country architecture for epidemic preparedness

Five recommendations for strengthening health security at the country level—developed and refined hand-in-hand with governments and partners.
A research agenda for urban health security

In a perspective piece published in Frontiers in Sustainable Cities, Resolve to Save Lives and partners outline ten key themes for strengthening health security in urban environments. Given cities’ unique vulnerabilities to infectious diseases, the paper highlights areas such as community partnerships, governance and financing, risk communication and resilient infrastructure as critical for epidemic preparedness. […]
Development of a Subnational Health Security Capacities Assessment Tool: Lessons From Nigeria and Implications for the Implementation of the Integrated Disease Surveillance and Response Strategy

In a study published in Health Security, Resolve to Save Lives and partners introduce a tool for assessing subnational health security in Nigeria that evaluates state-level capacities under the International Health Regulations (2005) (IHR). With input from public health leaders and legal experts, the team used a legislative evaluation to determine feasible IHR activities within […]
Using timeliness metrics for household contact tracing and TB preventive therapy
Can 7-1-7 help household contacts of tuberculosis patients get started on preventive therapy? In the International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, our colleagues at International Union Against Tuberculosis and Lung Disease used a mixed-methods approach to assess the feasibility of the timeliness metric in the private sector in Chennai, India. Among 263 index patients, […]
7-1-7: rapid improvement for early disease detection and response

Introductory brief on the 7-1-7 target, its uses, and how it complements existing tools and assessments.
7-1-7 for Accountability, Monitoring and Evaluation

The simplicity of 7-1-7’s timeliness metrics helps monitor performance, evaluate interventions and document progress with full transparency.
Advocacy as easy as 7-1-7
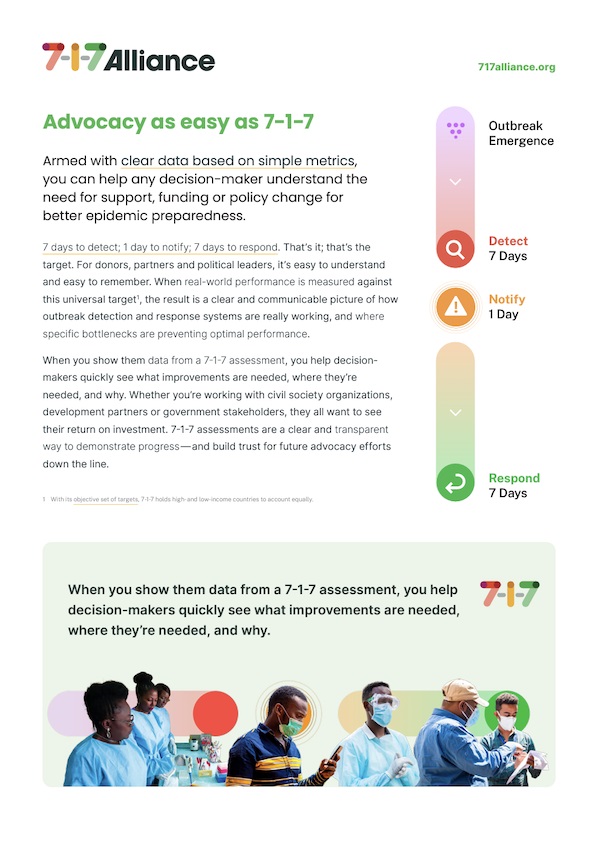
Clear data based on simple metrics can help any decision-maker understand the need for support, funding or policy change for better epidemic preparedness.
Continuous improvement with 7-1-7

By incorporating 7-1-7 into existing workflows, we can make every outbreak an opportunity to improve how we detect and respond to infectious disease threats.
Why 7-1-7? The evidence behind the global target for containing epidemic threat

Overview of the 7-1-7 evidence base.
Overview of the 7-1-7 Alliance

Introductory brief on the7-1-7 Alliance, the 7-1-7 target, and the Alliance missions.
Digital toolkit

Step-by-step guidance and tools to start putting 7-1-7 to work, in one place.
Protéger le Personnel de Santé: Il est Urgent D’agir

Dossier d’information sur la protection du personnel de santé pendant les épidémies.
PMEP Application

Zip file with PMEP application details and documents.
Rapid Outbreak Financing to Prevent Epidemics

An overview of how rapid outbreak financing are crucial to preventing epidemics.
Program Management for Epidemic Preparedness

An overview of program management for epidemic preparedness and how to strengthen health security through shared learning and peer exchange.
PERC Briefing on Economic Burden of COVID-19

A brief from PERC’s 24,000-person survey conducted in 18 African Union (AU) Member States in August 2020 to assess the household-level economic burden of COVID-19.
Prévention des Épidémies Ce que les Communautés, les Pays et le Monde Peuvent Faire Pour Progresser

Fiche d’information sur les actions clés pour faire progresser la prévention des épidémies.