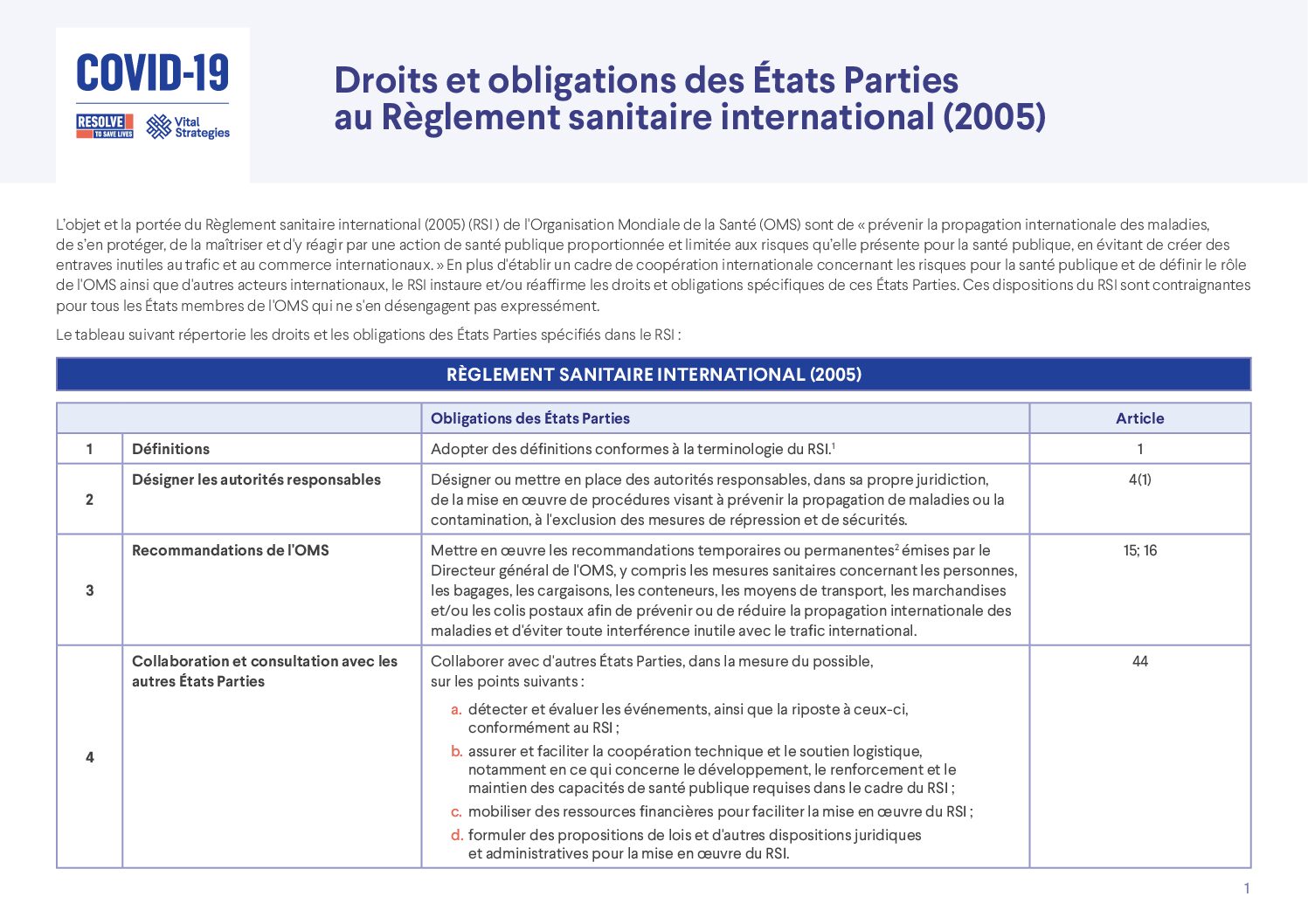
Resource Library
Brief
Resolve to Save Lives
Resolve to Save Lives
Resolve to Save Lives
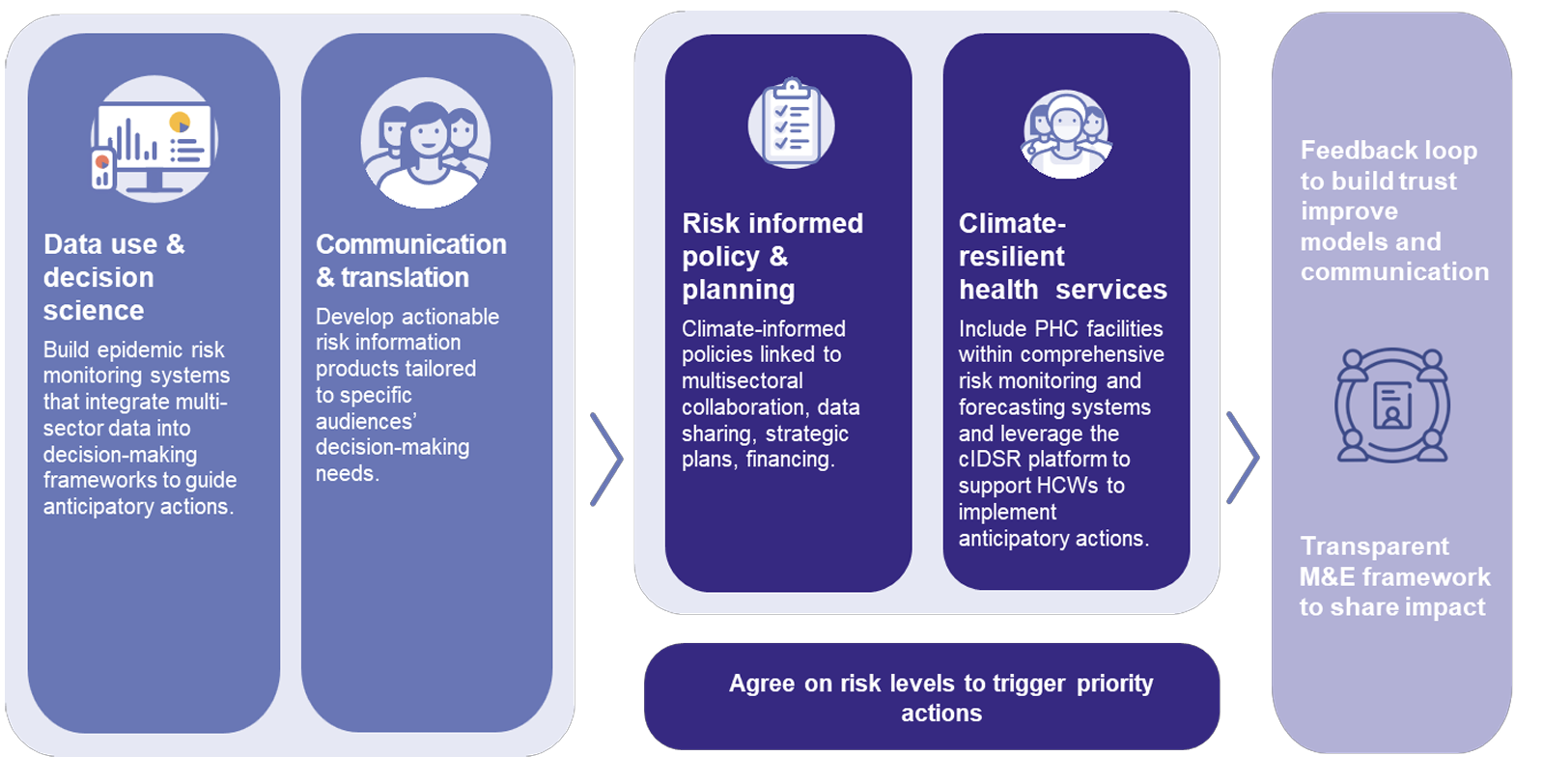
Strengthening epidemic readiness by integrating climate data into health systems.
7-1-7 Alliance
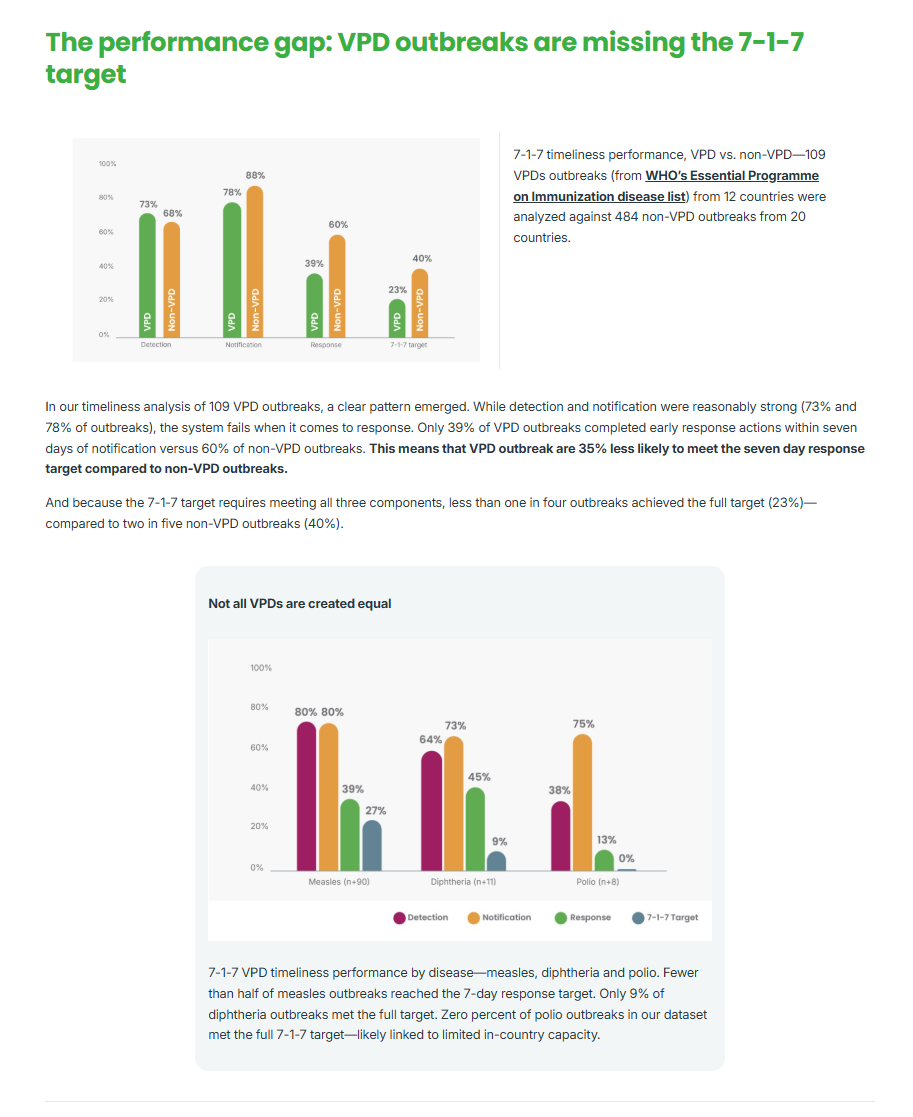
Find out how these 18 countries are leveraging 7-1-7 bottleneck data to prioritize investments and contain outbreaks faster.
7-1-7 Alliance
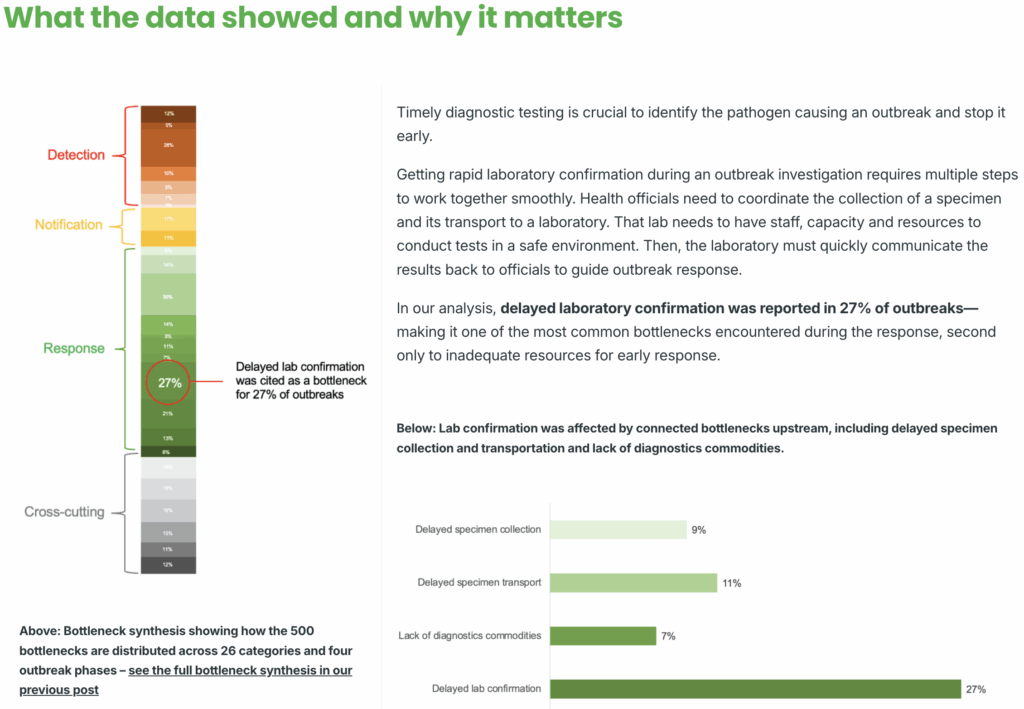
Solutions to a common 7-1-7 bottleneck: lack of available resources to initiate outbreak response.
7-1-7 Alliance
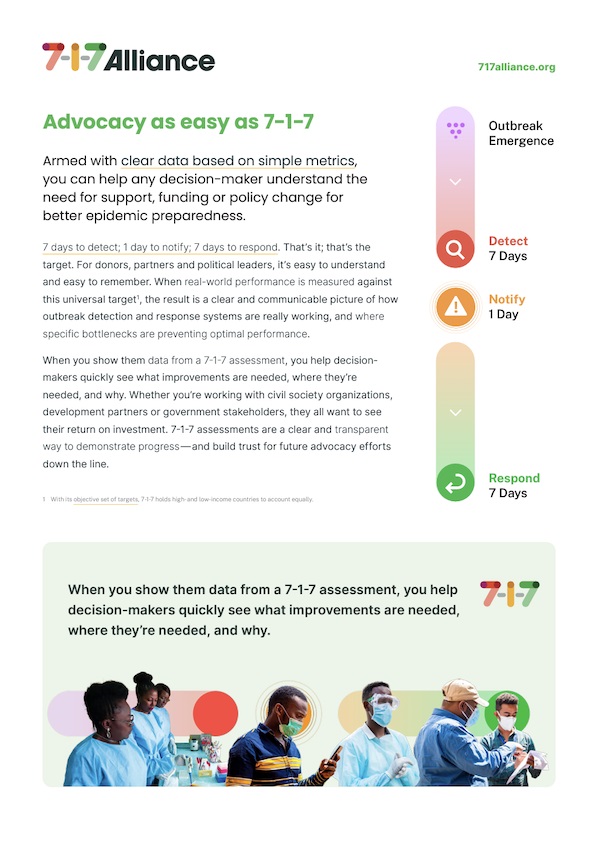
An introduction to the 7-1-7 target, its uses, and how it complements existing tools and assessments.
7-1-7 Alliance
7-1-7 Alliance
7-1-7 Alliance
7-1-7 Alliance
Resolve to Save Lives
Resolve to Save Lives
Resolve to Save Lives
Resolve to Save Lives
Resolve to Save Lives
Resolve to Save Lives
Resolve to Save Lives
Resolve to Save Lives
Resolve to Save Lives
Resolve to Save Lives
With adequate funding, clear roles and strong relationships, sufficient independence, an appropriate scope and the right people, NPHIs can improve health security and accelerate health progress.
Resolve to Save Lives
Resolve to Save Lives
Resolve to Save Lives
Resolve to Save Lives